Related articles
Shell
- Pendant - Ashmolean Museum
Stela -
Intef from his chapel at Abydos north - British Museum
Statue - headless - Metropolitan Museum
Temple - el-Tod treasure
Writing - Tale of Sinuhe written on Ostrica - British Museum
Royal Titulary
Senusret I, ruled
during the Middle Period, 12th Dynasty,
1956-1911 BC
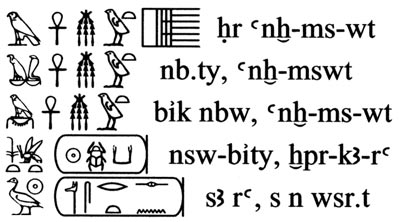
Horus name: Horus, Living of BirthsNebty Name: Two Ladies, living of Births
Golden Horus Name: Golden Falcon, Living of Births
Prenomen: King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Ka of Re has come to life
Nomen: Son of Re, Man of the Strong One
Shell
- Pendant - Fitzwilliam Museum
Seal - Cylinder inscribed with cartouche of Senusret I - Petrie Museum
Stela - Ity a high official - British Museum
Stela -
Intef - British
Museum
Stela - Samontu dating to the 12th Dynasty - British Museum
Stela - Senusret
being blessed by the god Horus from Buhen - Ashmolean Museum
Stela -
Mentuwoser - Metropolitan Museum
Stela - Rmry from
the temple of Satis on the Island of Elephantine - Manchester Museum
Statue - Lady Sennuwy from Kerma (tumulus K III) originally from Egypt (possibly Asyut) - Boston Museum
Statue - carved
from Limestone and from the temple of Amun in Karnak - Luxor Museum
Statue - with white crown - Cairo Museum
Statue - with
red crown - Metropolitan Museum
Statue - Grey granite, with Ramesses II and Merenptah
cartouche added to the back - Cairo Museum
Statue -
possibly dating to Senusret I - Metropolitan Museum
Statue - Mentuhotep "Chief of Police" from Lisht - Metropolitan Museum
Temple -
Edfu replaced
Senusret's structure
Temple - Door
jamb from Koptos - Ashmolean Museum
Temple - Jackal-headed souls of Nekhen and the hawk-headed souls of Pe - Metropolitan Museum
Temple - Scene of Senusret celebrating his
Heb-Sed -
Metropolitan Museum
Temple -
Limestone
fragments from a pylon - Liverpool Museum
Writing - Tale of Sinuhe written on Ostrica - Ashmolean Museum
Each King created a name on his ascension to the throne and it was
also a 'mandate' for this style of leadership. The royal name was comprised of 5 separate elements (although earlier
kings used less) we modern writing often used the 'Nomen' or person name, which preceded his kingship.
The full titulary was only used in formal inscriptions; otherwise a king was
usually identified by his Prenomen which was either written alone or accompanied
by the Nomen. The Prenomen and Nomen are usually left in their Egyptian forms (for example, 'Thutmose' rather than
translating it into 'Thoth-is-born'). The transliteration of the kings' names vary in modern books on Egyptology. Some
retain the Graecised form of a name (but this is now less common and a
translation from the original hieroglyphs is used), as it occurred in the historical account of Manetho (e.g., Amenophis, Sesostris,
Cheops), whereas others give a translation based on the Hieroglyphs (e.g., Amenhotep, Senusret, Khufu). Pronunciations
also vary, because of the absence of vowels in the hieroglyphic writings of the names and our limited knowledge of the
pronunciation of Ancient Egyptian.
'Nebty' name
Nbty means the 'Two Ladies', and this name emphasises
the king's special relationship with the two great goddesses, Nekhbet, the vulture goddess of Upper Egypt, and Edjo, the
cobra goddess of Lower Egypt . They ruled supreme as the two ancient capitals of Hieraconpolis and Pe, before Egypt was
unified by King Menes in c. 3100 BC. However, they continued to play an important role as royal protectress even after
unification - hence their inclusion in the royal titulary.
Golden Horus name
The meaning of this name is uncertain. It may signify the victory of Horus over his enemy Seth (in
the myth of Osiris), but it may represent the reconciled enemies, Horus and Seth, as lords of Egypt .
Prenomen
Nomen
The Nomen, again enclosed within a cartouche, was usually the name of the king before he succeeded to
the throne (i.e. almost a family name) and therefore, it is not uncommon for several kings within a family to have the
same Nomen (e.g. Thutmose, Amenhotep, Senusret). The Nomen was immediately preceded (outside the cartouche) by the title
sA ra ('son of Re').