
| Ancient Egypt and Archaeology Web Site |

| Period | Dynasty | Period | Dynasty | ||
| Palaeolithic | New Kingdom | 18th Dynasty | |||
| Saharan Neolithic | Ramesside | 19th Dynasty | |||
| Pre-Dynastic | 20th Dynasty | ||||
| Early Dynastic | 1st Dynasty | Third Intermediate | 21st Dynasty | ||
| 2nd Dynasty | 22nd Dynasty | ||||
| Old Kingdom | 3rd Dynasty | 23rd Dynasty | |||
| 4th Dynasty | 24th Dynasty | ||||
| 5th Dynasty | 25th Dynasty | ||||
| 6th Dynasty | Late | 26th Dynasty | |||
| 7th and 8th Dynasties | 27th Dynasty (1st Persian Period) | ||||
| First Intermediate | 9th and 10th Dynasties | 28th Dynasty | |||
| 11th Dynasty Thebes only | 29th Dynasty | ||||
| Middle Kingdom | 11th Dynasty All of Egypt | 30th Dynasty | |||
| 12th Dynasty | 31st Dynasty (2nd Persian Period) | ||||
| 13th Dynasty | Ptolemaic | Ptolemaic Dynasty | |||
| 14th Dynasty | Roman | ||||
| Second Intermediate | 15th Dynasty (Hyksos) | ||||
| 16th Dynasty | Coptic | ||||
| 17th Dynasty | Islamic | ||||
|
Source:
|
|||||
| EARLY DYNASTIC PERIOD | 1st Dynasty c.3000-2890 | Aha |
|
|
| c.3000-2686 | Djer |
|
||
| Djet |
|
|||
| Den |
|
|||
| Queen Merneith |
|
|||
| Anedjib |
|
|||
| Semerkhet |
 |
|||
| Qa'a |
|
|||
| 2nd Dynasty 2890-2686 | Hetepsekhemwy |
 |
||
| Raneb |
|
|||
| Nynetjer |
|
|||
| Weneg | ||||
| Sened | ||||
| Peribsen |
 |
|||
| Khasekhemwy |
.jpg) |
|||
| OLD KINGDOM | 3rd Dynasty 2686-2613 | Nebka | 2686-2667 | |
| 2686-2160 | Djoser (Netjerikhet) |
|
2667-2648 | |
| Sekhemkhet |
|
2648-2640 | ||
| Khaba | 2640-2637 | |||
| Huni | 2637-2613 | |||
| 4th Dynasty 2613-2494 | Sneferu |
|
2613-2589 | |
| Khufu (Cheops) |
|
2589-2566 | ||
| Djedefra (Radjedef) |
|
2566-2558 | ||
| Khafra (Chephren) |
|
2558-2532 | ||
| Menkaura (Mycerinus) |
|
2532-2503 | ||
| Shepseskaf |
|
2503-2494 | ||
| 5th Dynasty 2494-2345 | Userkaf |
|
2494-2487 | |
| Sahura |
|
2487-2475 | ||
| Neferirkara | 2475-2455 | |||
| Shepseskara |
|
2455-2448 | ||
| Raneferef or Nefer-ef-Ra | 2448-2445 | |||
| Nyuserra | 2445-2421 | |||
| Menkauhor | 2421-2414 | |||
| Djedkara | 2414-2375 | |||
| Unas |
|
2375-2345 | ||
| 6th Dynasty 2345-2181 | Teti |
|
2345-2323 | |
| Userkara [a usurper] | 2323-2321 | |||
| Pepy I (Meryra) |
|
2321-2287 | ||
| Merenra | 2287-2278 | |||
| Pepy II (Neferkara) |
|
2278-2184 | ||
| Nitiqret | 2184-2181 | |||
| 7th and 8th Dynasties 2181-2160 | Numerous kings, called Neferkara, presumably imitating Pepy II. | |||
| FIRST INTERMEDIATE PERIOD | 9th and 10th Dynasties (Herakleopolitan) 2160-2025 | Khety (Meryibra) |
|
|
| 2160-2055 | Khety (Nebkaura) | |||
| Khety (Wahkara) |
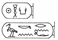 |
|||
| Merykara |
|
|||
|
Intef I (Sehertawy) |
|
||
| Intef II (Wahankh) |
|
|||
| Intef III (Nakhtnebtepnefer) |
|
|||
| MIDDLE KINGDOM | 11th Dynasty 2055-1985 | Mentuhotep II (Nebhepetra) |
|
2055-2004 |
| 2055-1650 | (all Egypt) | Mentuhotep III (Sankhkara) |
|
2004-1992 |
| Mentuhotep IV (Nebtawyra) |
|
1992-1985 | ||
| 12th Dynasty 1985-1773 | Amenemhat I (Sehetepibra) |
|
1985-1956 | |
| Senusret I (Kheperkara) |
|
1956-1911 | ||
| Amenemhat II (Nubkaura) |
|
1911-1877 | ||
| Senusret II (Khakheperra) |
|
1877-1870 | ||
| Senusret III (Khakaura) |
|
1870-1831 | ||
| Amenemhat III (Nimaatra) |
|
1831-1786 | ||
| Amenemhat IV (Maakherura) |
|
1786-1777 | ||
| Queen Sobekneferu (Sobekkara) | 1777-1773 | |||
| 13th Dynasty 1773-after 1650 | Wegaf (Khutawyra) |
 |
||
| Sobekhotep II (Sekhemra-khutawy) | ||||
| Iykhernefert Neferhotep (Sankhta sekhemra) | ||||
| Ameny-intef-amenemhat (Sankhibra) | ||||
| Hor (Awibra) |
|
|||
| Khendjer (Userkara) |
|
|||
| Sobekhotep III (Sekhemra-sewadjtawy) | ||||
| Neferhotep I (Khasekhemra) |
|
|||
| Sahathor | ||||
| Sobekhotep IV (Khaneferra) |
|
|||
| Sobekhotep V |
|
(?) | ||
| Ay (Merneferra) |
|
|||
| 14th Dynasty c.1773-1650 | Minor rulers probably contemporary with the 13th or 15th Dynasty | |||
| SECOND INTERMEDIATE PERIOD | 15th Dynasty (Hyksos) 1650-1550 | Salitis/Sekerher | c.1555 | |
| 1650-1550 | Khyan (Seuserenra) |
|
c.1600 | |
| Apepi (Aauserra) | c.1555 | |||
| Khamudi | ||||
| 16th Dynasty c.1650-1580 | Theban early rulers contemporary with the 15th Dynasty | |||
| 17th Dynasty c.1580-1550 | Rahotep | |||
| Sobekemsaf I | ||||
| Intef VI (Sekhemra) | ||||
| Intef VII (Nubkheperra) |
|
|||
| Intef VIII (Sekhemraherhermaat) | ||||
| Sobekemsaf II | ||||
| Siamun |
|
|||
| Taa (Senakhtenra/Seqenenra) |
|
c.1560 | ||
| Kamose (Wadjkheperra) |
|
1555-1550 | ||
| NEW KINGDOM | 18th Dynasty 1550-1295 | Ahmose (Nebpehtyra) |
|
1550-1525 |
| 1550-1069 | Amenhotep I (Djeserkara) |
|
1525-1504 | |
| Thutmose I (Aakheperkara) |
|
1504-1492 | ||
| Thutmose II (Aakheperenra) |
|
1492-1479 | ||
| Thutmose III (Menkheperra) |
|
1479-1425 | ||
| Queen Hatshepsut (Maatkara) |
|
1473-1458 | ||
| Amenhotep II (Aakheperura) |
|
1427-1400 | ||
| Thutmose IV (Menkheperura) |
|
1400-1390 | ||
| Amenhotep III (Nebmaatra) |
|
1390-1352 | ||
| Amenhotep IV/Akhenaten (Neferkheperurawaenra) |
|
1352-1336 | ||
| Neferneferuaten (Smenkhkara) |
|
1338-1336 | ||
| Tutankhamun (Nebkheperura) |
|
1336-1327 | ||
| Ay (Kheperkheperura) |
|
1327-1323 | ||
| Horemheb (Djeserkheperura) |
|
1323-1295 | ||
| RAMESSIDE PERIOD | 19th Dynasty 1295-1186 | Ramesses I (Menpehtyra) |
|
1295-1294 |
| 1295-1069 | Sety I (Menmaatra) |
|
1294-1279 | |
| Ramesses II (Usermaatra Setepenra) |
|
1279-1213 | ||
| Merenptah (Baenra) |
|
1213-1203 | ||
| Amenmessu (Menmira) |
|
1203-1200 | ||
| Sety II (Userkheperura Setepenra) |
|
1200-1194 | ||
| Siptah (Akehnrasetepenra) |
|
1194-1188 | ||
| Queen Tausret (Sitrameritamun) |
|
1188-1186 | ||
| 20th Dynasty 1186-1069 | Sethnakht (Userkhaura Meryamun) |  |
1186-1184 | |
| Ramesses III (Usermaatra Meryamun) |
 |
1184-1153 | ||
| Ramesses IV (Heqamaatra Setepenamun) |
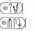 |
1153-1147 | ||
| Ramesses V (Usermaatra Sekheperenra) | 1147-1143 | |||
| Ramesses VI (Nebmaatra Meryamun) |
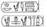 |
1143-1136 | ||
| Ramesses VII (Usermaatra Setepenra Meryarnun) | 1136-1129 | |||
| Ramesses VIII (UsermaatraAkhenamun) | 1129-1126 | |||
| Ramesses IX (Neferkara Setepenra) |
 |
1126-1108 | ||
| Ramesses X (Khepermaatra Setepenra) | 1108-1099 | |||
| Ramesses XI (Menmaatra Setepenptah) |
 |
1099-1069 | ||
| THIRD INTERMEDIATE PERIOD | 21st Dynasty 1069-945 (in Tanis) | Smendes (Hedjkheperra Setepenra) | 1069-1043 | |
| 1069-664 | Amenemnisu (Neferkara) | 1043-1039 | ||
| Psusennes I [Pasebakhaenniut] (Akheperra Setepenamun) |
 |
1039-991 | ||
| Amenemope (Usermaatra Setepenamun) |
|
993-984 | ||
| Osorkon the Elder (Akheperra setepenra) | 984-978 | |||
| Siamun (Netjerkheperra Setepenamun) |
|
978-959 | ||
| Psusennes II [Pasebakhaenniut] (Titkheperura Setepenra) |
|
959-945 | ||
| 22nd Dynasty 945-715 (in Bubastis) | Sheshonq I (Hedjkheperra) |
|
945-924 | |
| (Rulers at Tanis) | Osorkon I (Sekhemkheperra) |
|
924-889 | |
| Sheshonq II (Heqakheperra) |
|
c.890 | ||
| Takelot I | 889-874 | |||
| Osorkon II (Usermaatra) |
|
874-850 | ||
| Takelot II (Hedjkheperra) |
|
850-825 | ||
| Sheshonq III (Usermaatra) |
|
825-773 | ||
| Pimay (Usermaatra) | 773-767 | |||
| Sheshonq V (Aakheperra) | 767-730 | |||
| Osorkon IV (Aakheperra) | 730-715 | |||
| 23rd Dynasty 818-715 (in Leontopolis) | Kings in various centres, contemporary with the later 22nd, 24th, and early 25th dynasties, including: | |||
| Pedubastis I (Usermaatra) | ||||
| Iuput I |
|
|||
| Sheshonq IV | ||||
| Osorkon III (Usermaatra) | ||||
| Takelot III (Usermaatra) | ||||
| Rudamon (Usermaatra) | ||||
| Peftjauawybast | ||||
| Iuput II (Usermaatra) | ||||
| 24th Dynasty 727-715 (in Sais) | Bakenrenef (Bocchoris) | 720-715 | ||
| 25th Dynasty 747-656 (in Napata) | Piy (Menkheperra) | 747-716 | ||
| Shabago (Neferkara) |
|
716-702 | ||
| Shabitgo(Djedkaura) |
|
702-690 | ||
| Taharqo (Khunefertemra) |
|
690-664 | ||
| Tanutamani (Bakara) |
|
664-656 | ||
|
26th Dynasty 664-525 | Nekau I |
|
672-664 |
| (The Saites) | Psamtek I (Wahibra) |
|
664-610 | |
| Nekau II (Wehemibra) | 610-595 | |||
| Psamtek II (Neferibra) |
|
595-589 | ||
| Apries (Haaibra) |
|
589-570 | ||
| Ahmose II [Amasis] (Khnemibra) |
|
570-526 | ||
| Psamtek III (Ankhkaenra) |
|
526-525 | ||
| 27th Dynasty 525-404 | Cambyses |
|
525-522 | |
| (1st Persian Period) | Darius I |
|
522-486 | |
| Xerxes I |
|
486-465 | ||
| Artaxerxes I |
|
465-424 | ||
| Darius II | 424-405 | |||
| Artaxerxes II | 405-359 | |||
| 28th Dynasty 404-399 | Amyrtaios | 404-399 | ||
| 29th Dynasty 399-380 | Nepherites I [Nefaarud] |
 |
399-393 | |
| Hakor [Achoris] (Khnemmaatra) |
 |
393-380 | ||
| Nepherites II | c.380 | |||
| 30th Dynasty 380-343 | Nectanebo I (Kheperkara) |
 |
380-362 | |
| (2nd Persian Period) | Teos (Irma atenra) |
|
362-360 | |
| Nectanebo II (Senedjemibra setepenanhur) |
 |
360-343 | ||
| 31st Dynasty 343-332 | Artaxerxes III Ochus | 343-338 | ||
| Arses | 338-336 | |||
| Darius III Codoman |
|
336-332 | ||
|
Macedonian Dynasty 332-305 | Alexander the Great |
 |
332-323 |
| Philip Arrhidaeus |
|
323-317 | ||
| Alexander IV (note 4) |
|
317-310 | ||
| Ptolemaic Dynasty 305-30 | Ptolemy I Soter I |
|
305-285 | |
| Ptolemy II Philadelphus |
|
285-246 | ||
| Ptolemy III Euergetes I |
|
246-221 | ||
| Ptolemy IV Philopator |
|
221-205 | ||
| Ptolemy V Epiphanes |
|
205-180 | ||
| Ptolemy VI Philometor | 180-145 | |||
| Ptolemy VII Neos Philopator | 145 | |||
| Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II | 170-116 | |||
| Ptolemy IX Soter II | 116-107 | |||
| Ptolemy X Alexander I | 107-88 | |||
| Ptolemy IX Soter II (restored to thrown) | 88-80 | |||
| Ptolemy XI Alexander II | 80 | |||
| Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysos (Auletes) |
|
80-51 | ||
| Cleopatra VII Philopator |
|
51-30 | ||
| Ptolemy XIII | 51-47 | |||
| Ptolemy XIV | 47-44 | |||
| Ptolemy XV Caesarion |
|
44-30 | ||
|
Augustus |
|
30 -AD 14 | |
| Tiberius |
|
AD 14-37 | ||
| Gains (Caligula) | AD 37-41 | |||
| Claudius | AD 41-54 | |||
| Nero | AD 54-68 | |||
| Galba | AD 68-69 | |||
| Otho | AD 69 | |||
| Vespasian | AD 69-79 | |||
| Titus | AD 79-81 | |||
| Domitian |
|
AD 81-96 | ||
| Nerva | AD 96-98 | |||
| Trajan |
|
AD 98-117 | ||
| Hadrian |
|
AD 117-138 | ||
| Antoninus Pius | AD 138-161 | |||
| Marcus Aurelius | AD 161-180 | |||
| Lucius Verus | AD 161-169 | |||
| Commodus | AD 180-192 | |||
| Septimius Severus | AD 193-211 | |||
| Caracalla | AD 198-217 | |||
| Geta | AD 209-212 | |||
| Macrinus | AD 217-218 | |||
| Didumenianus | AD 218 | |||
| Severus Alexander | AD 222-235 | |||
| Gordian III | AD 238-242 | |||
| Philip | AD 244-249 | |||
| Decius | AD 249-251 | |||
| Gallus and Volusianus | AD 251-253 | |||
| Valerian | AD 253-260 | |||
| Gallienus | AD 253-268 | |||
| Macrianus and Quietus | AD 260-261 | |||
| Aurelian | AD 270-275 | |||
| Probus | AD 276-282 | |||
| Diocletian |
|
AD 284-305 | ||
| Maximian | AD 286-305 | |||
| Galerius | AD 293-311 | |||
| Constantius | AD 293-306 | |||
| Constantine I | AD 306-337 | |||
| Maxentius | AD 306-312 | |||
| Maximinus Daia | AD 307-324 | |||
| Licinius | AD 308-324 | |||
| Constantine II | AD 337-340 | |||
| Constans (co-ruler) | AD 337-350 | |||
| Constantius II (co-ruler) | AD 337-361 | |||
| Magnetius (co-ruler) | AD 350-353 | |||
| Julian the Apostate | AD 361-363 | |||
| Jovian | AD 363-364 | |||
| Valentinian I (west) | AD 364-375 | |||
| Valens (co-ruler, east) | AD 364-378 | |||
| Gratian (co-ruler, west) | AD 375-383 | |||
| Theodosius (co-ruler) | AD 379-395 | |||
| Valentinian II (co-ruler, west) | AD 383-392 | |||
| Eugenius (co-ruler) | AD 392-394 | |||
The full titulary was only used in formal inscriptions; otherwise a king was usually identified by
his prenomen which was either written alone or accompanied by the nomen. The prenomen and nomen are usually left in their Egyptian forms (for example, 'Thutmose' rather than
translating it into 'Thoth-is-born'). The transliteration of the kings' names vary in modern books on Egyptology. Some
retain the Graecised form of a name, as it occurred in the historical account of Manetho (e.g., Amenophis, Sesostris,
Cheops), whereas others give a translation based on the Hieroglyphs (e.g., Amenhotep, Senusret, Khufu). Pronunciations
also vary, because of the absence of vowels in the hieroglyphic writings of the names and our limited knowledge of the
pronunciation of Ancient Egyptian.
Horus name
- This name was often written within a rectangular frame, on top of which perched the falcon-god Horus,
which probably represented the king's palace. This name represented the king as the earthly incarnation of the ancient
falcon-god Horus, who became the first divine patron of royalty.
'Nebty' name - Nbty means the 'Two Ladies', and this name emphasises
the king's special relationship with the two great goddesses, Nekhbet, the vulture goddess of Upper Egypt, and Edjo, the
cobra goddess of Lower Egypt . They ruled supreme as the two ancient capitals of Hieraconpolis and Pe, before Egypt was
unified by King Menes in c.3100 BC. However, they continued to play an important role as royal protectress even after
unification - hence their inclusion in the royal titulary.
Royal Titulary
Each King created a name on his ascension to the throne and it was
also a 'mandate' for this style of leadership. The royal name was comprised of 5 separate elements (although earlier
kings used less) we modern writing often used the 'Nomen' or person name, which preceded his kingship. Many Egyptian
names were translated into Greek, for example Amenhotep (Egyptian) into Amenophis (Greek)
- older books tend to use the Greek names but this is now less common and a translation from the original hieroglyphs is
used.
Golden Horus name - The meaning of this name is uncertain. It may signify the victory of Horus over his enemy Seth (in the myth of Osiris), but it may represent the reconciled enemies, Horus and Seth, as lords of Egypt .
Prenomen - From the 5th Dynasty onwards (after King Sahure), the Prenomen and the Nomen were both written inside cartouches. The prenomen was adopted as a religious name by each king when he ascended to the throne, and it was always immediately preceded (outside the cartouche) by the title n-sw-bit 'he who belongs to the sedge and the bee'. The sedge represented Upper Egypt, and the bee Lower Egypt, so the title meant 'King of Upper and Lower Egypt '. The prenomen itself usually incorporates the name of the god Re (e.g. nb-mAat-re, 'Re is Lord of Truth').
Nomen - The nomen, again enclosed within a cartouche, was usually the name of the king before he succeeded to the throne (i.e. almost a family name) and therefore, it is not uncommon for several kings within a family to have the same nomen (e.g. Thutmose, Amenhotep, Senusret). The nomen was immediately preceded (outside the cartouche) by the title s3 ra ('son of Re').
There is a
Ancient Egyptian Dictionary
available for download (it is 2.9 Mbytes). Note - Don't forget that PDF files can be searched using Ctrl-F or
Shift-Ctrl-F (this is a good feature that lists all matches in a side window). This also works for Transliteration; e.g. to Find
![]() (Ancient Egyptian inscription for 'Friendly') you can search for sbT Hr (case insensitive) using the
Manual de Codage system. The
same applies for the Gardiner (see full sign list),
which are separated by a dash.
(Ancient Egyptian inscription for 'Friendly') you can search for sbT Hr (case insensitive) using the
Manual de Codage system. The
same applies for the Gardiner (see full sign list),
which are separated by a dash.
Note - If you can't see an S with an upside down V above it inside the brackets (S) then you need some additional fonts for your PC. Here is a link to the font file, which can install or save (into your font directory, often c:\windows\Fonts\). You will need to re-load this page to see the new fonts.